Heap & Graph
Heap & Graph Search Algorithms |
Heap
<font size = 2.5>
Heap: is an unsorted array but have special rules to follow Heapify(数组建堆 时间复杂度O(n)): https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/building-heap-from-array/
//新建小根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
//新建大根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer num1, Integer num2) {
return num2 - num1;
}
});
性质:堆的实现通过构造二叉堆(binary heap),这种数据结构具有以下性质
- 任意节点小于它的所有后裔,最小元素在堆的根上 (增序性)。
- 堆总是一颗完全树。Complete tree
- 将根节点最大的堆叫做MAX HEAP, 根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆MIN HEAP
- Index of lChild = index of parent X 2 + 1
- Index of rChild = index of parent X 2 + 2
- Unsorted but follow rules above
支持的基本操作:
- Insert: 向堆中植入一个新元素;时间复杂度o(log(n)) insert 0
- Update: 将新元素提升使其符合堆的性质, 时间复杂度o(log(n)) 4 -> -4 3 -> 13
- Get/top: 获取当前堆顶元素的值;时间复杂度o(1)
- Pop: 删除堆顶元素; 时间复杂度o(log(n))
- Heaplfy: 使用一个unsorted array变成一个堆。时间复杂度o(n)
Example
1.未排序数组中最小的k位数。 Find smallest k elements from an unsorted array of size n. JAVA实现
//方法一:排序后取前k位
class Solution {
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
int[] vec = new int[k];
Arrays.sort(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
vec[i] = arr[i];
}
return vec;
}
}
//方法二:堆
//1. minHeap
class Solution {
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
int[] result = new int[k];
// Corner case
if (k == 0) return result;
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
minHeap.offer(arr[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result[i] = minHeap.poll();
}
return result;
}
}
//2. maxHeap
class Solution {
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
int[] result = new int[k];
if (k == 0) { // 排除 0 的情况
return result;
}
//java priority queue默认小根堆,实现大根堆需要重写一下比较器。
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer num1, Integer num2) {
return num2 - num1;
}
});
/**
实现大根堆也可以写成:
PriorityQueue<Integer>priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
});
**/
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
maxHeap.offer(arr[i]);
}
for (int i = k; i < arr.length; ++i) {
if (maxHeap.peek() > arr[i]) {
maxHeap.poll();
maxHeap.offer(arr[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
result[i] = maxHeap.poll();
}
return result;
}
}
题解地址: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zui-xiao-de-kge-shu-lcof/solution/jian-zhi-offer-40-zui-xiao-de-k-ge-shu-j-9yze/
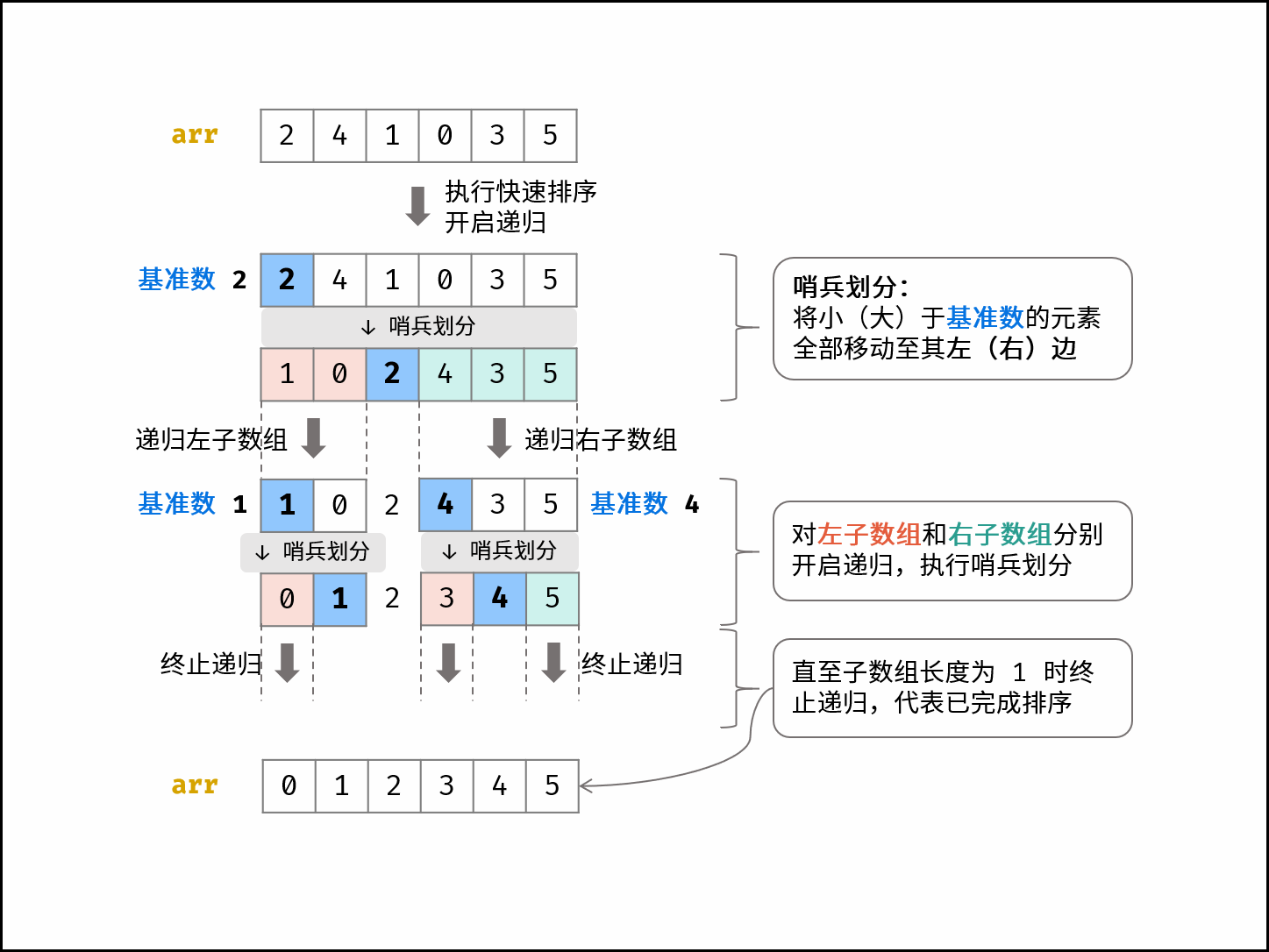
//快排
class Solution {
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
//返回数组的前k个值
//对于原始数组和新数组中有效的所有索引,两个数组将具有相同的值。
//如果复制的数组长度大于原始数组的长度,则原始索引中丢失的索引的副本数将为零。
return Arrays.copyOf(arr, k);
}
private void quickSort(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
// 子数组长度为 1 时终止递归
if (l >= r) return;
// 哨兵划分操作(以 arr[l] 作为基准数)
int i = l, j = r;
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && arr[j] >= arr[l]) j--;
while (i < j && arr[i] <= arr[l]) i++;
swap(arr, i, j);
}
swap(arr, i, l);
// 递归左(右)子数组执行哨兵划分
quickSort(arr, l, i - 1);
quickSort(arr, i + 1, r);
}
private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
</font>
Graph
<font size = 2.5>