Linked List
Linked List
JAVA构建方法
https://www.cnblogs.com/qifengshi/p/6401744.html
1.构建一个单向链表: java实现:
//方法1
//类名 :Java类就是一种自定义的数据结构
class ListNode {
//数据 :节点数据
int val;
//对象 :引用下一个节点对象。
//在Java中没有指针的概念
//Java中的引用和C语言的指针类似
ListNode next;
//构造方法 :构造方法和类名相同
ListNode(int val){
//把接收的参数赋值给当前类的val变量
this.val=val;
}
}
//范型写法
private static class Node<E>{
E item;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E item, Node<E> next, Node<E> prev) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
2.构建一个双向链表: java实现:
//方法1
//类名 :Java类就是一种自定义的数据结构
class ListNode {
//数据 :节点数据
int val;
//对象 :引用上一个节点对象
ListNode prev;
//对象 :引用下一个节点对象
ListNode next;
//构造方法 :构造方法和类名相同
ListNode(int val){
//把接收的参数赋值给当前类的val变量
this.val=val;
}
}
//范型写法
private static class Node<E>{
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
public Node(E item, Node<E> next, Node<E> prev) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
Example:
1.Reverse Linked List
图解文字讲解:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/solution/dong-hua-yan-shi-206-fan-zhuan-lian-biao-by-user74/
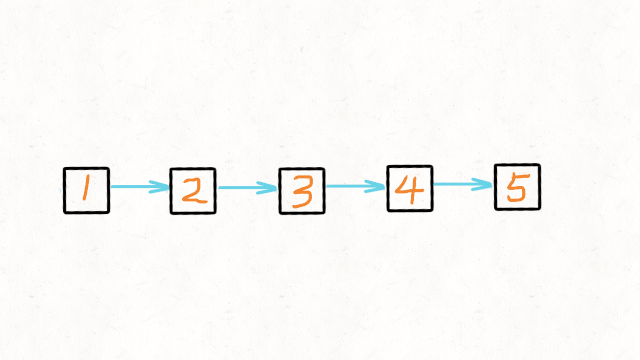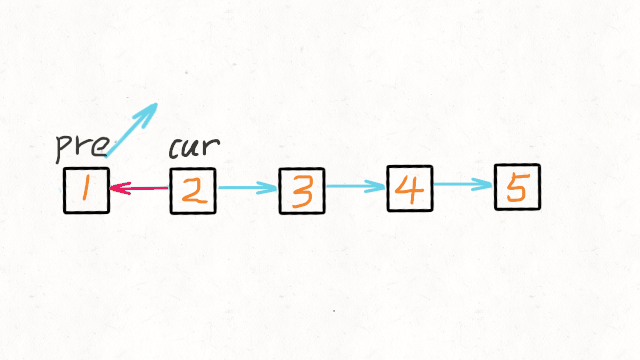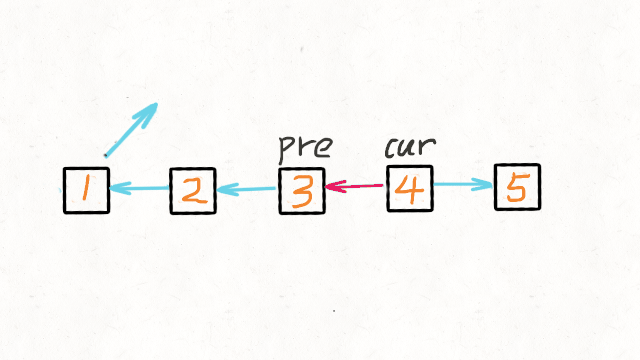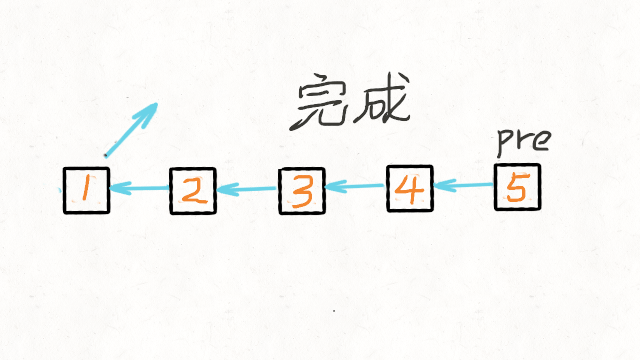
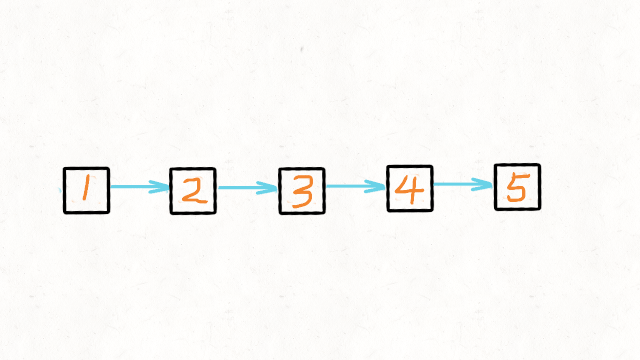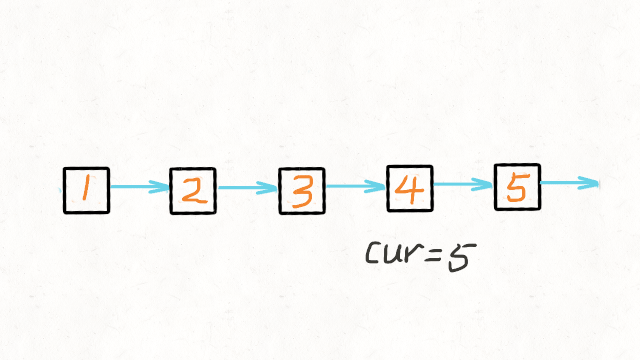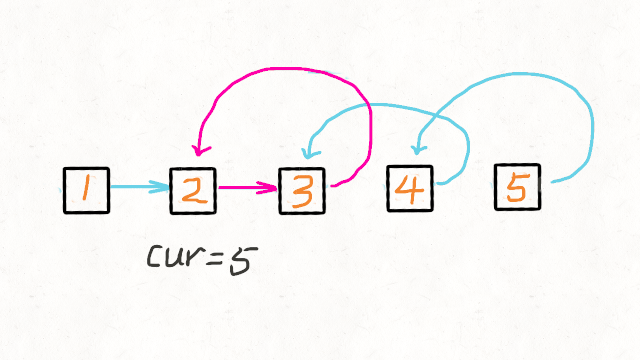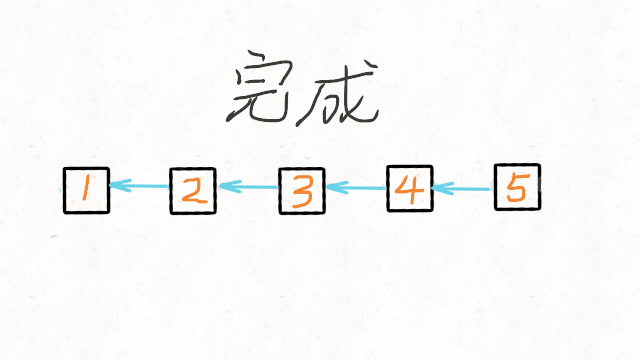 JAVA实现
JAVA实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
//方法1 Iterative双指针迭代
/**
* 双指针迭代
* 我们可以申请两个指针,第一个指针叫 pre,最初是指向 null 的。
* 第二个指针 cur 指向 head,然后不断遍历 cur。
* 每次迭代到 cur,都将 cur 的 next 指向 pre,然后 pre 和 cur 前进一位。
* 都迭代完了(cur 变成 null 了),pre 就是最后一个节点了。
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//申请节点,pre和 cur,pre指向null
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
//记录当前节点的下一个节点
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
//然后将当前节点指向pre
curr.next = prev;
//pre和cur节点都前进一位
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
}
//方法2 Recursive
/**
* 递归函数中每次返回的newHead其实只最后一个节点,在递归函数内部,改变的是当前节点的指向。
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//递归终止条件是当前为空,或者下一个节点为空
// Base case
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// Recursive rule
//这里的newHead就是最后一个节点
ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
//这里请配合动画演示理解
//如果链表是 1->2->3->4->5,那么此时的newHead就是5
//而head是4,head的下一个是5,下下一个是空
//所以head.next.next 就是5->4
head.next.next = head;
//防止链表循环,需要将head.next设置为空
head.next = null;
//每层递归函数都返回newHead,也就是最后一个节点
return newHead;
}
}
2.Middle of the Linked List
图解文字讲解:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/solution/kuai-man-zhi-zhen-zhu-yao-zai-yu-diao-shi-by-liwei/
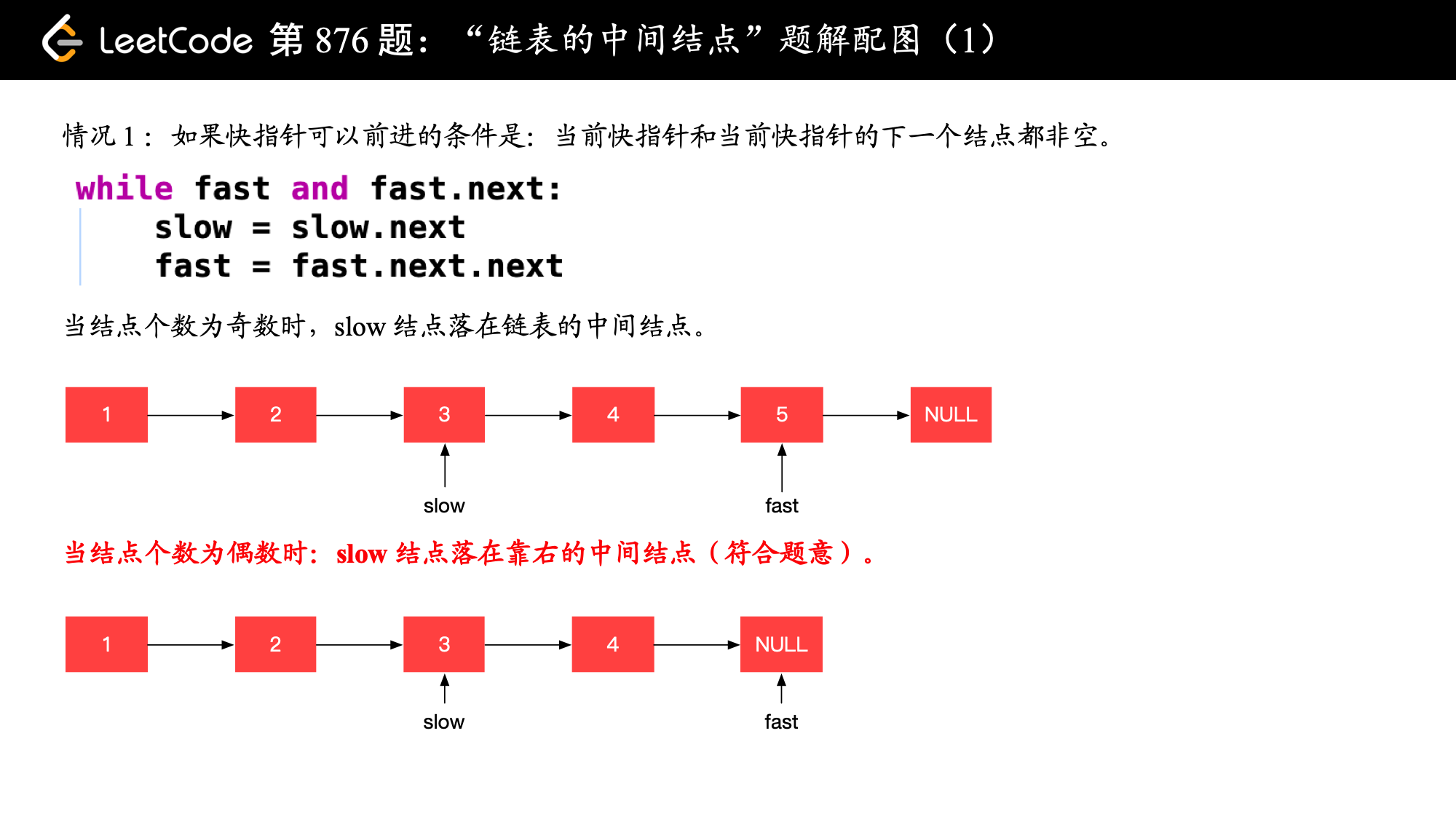
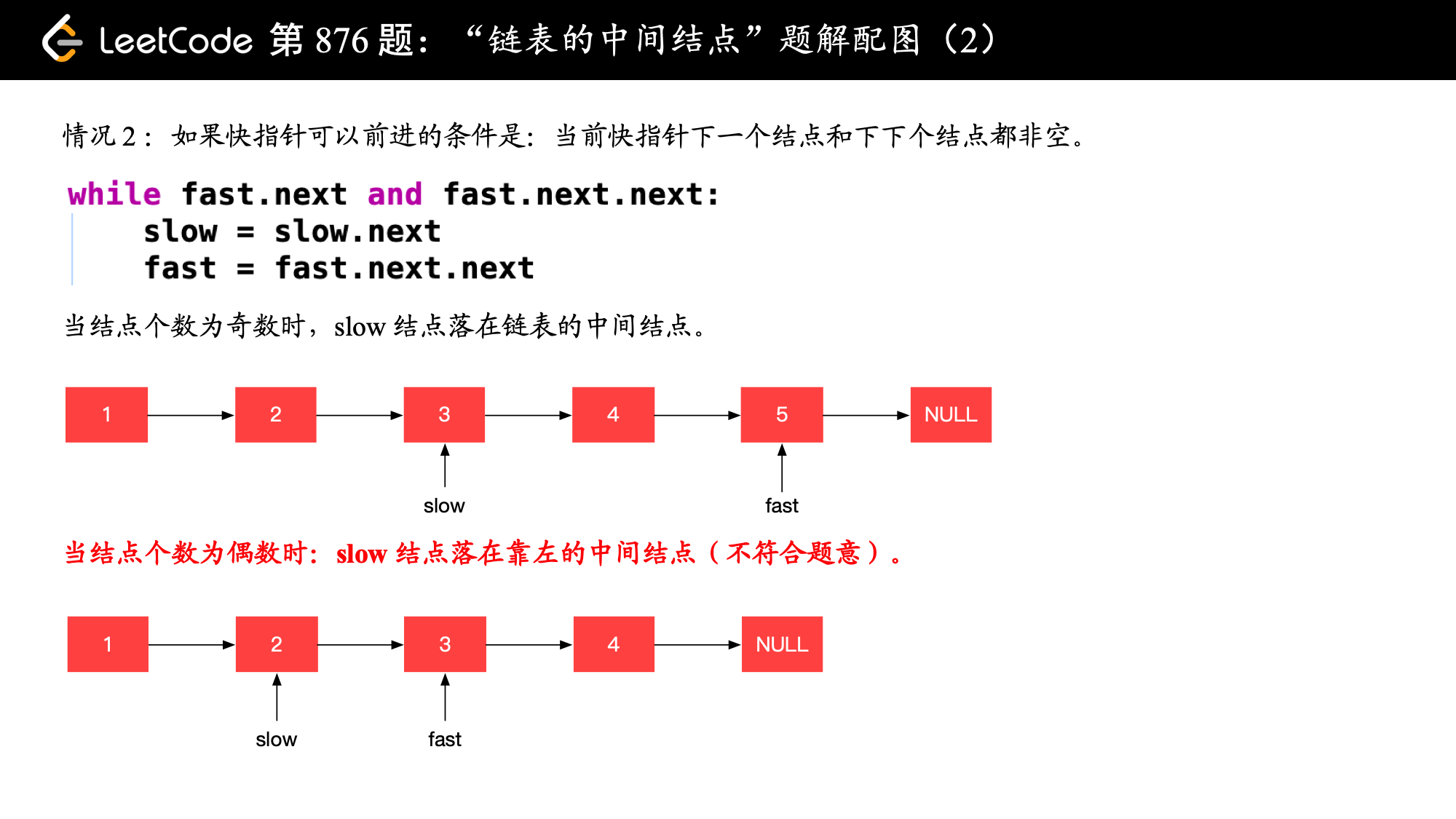 JAVA实现
JAVA实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
//题解:使用快慢指针
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
//完整代码
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
public ListNode(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("arr can not be empty");
}
this.val = nums[0];
ListNode curr = this;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
curr.next = new ListNode(nums[i]);
curr = curr.next;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
ListNode cur = this;
while (cur != null) {
s.append(cur.val);
s.append(" -> ");
cur = cur.next;
}
s.append("NULL");
return s.toString();
}
}
public class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
// int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
ListNode head = new ListNode(arr);
Solution solution = new Solution();
ListNode res = solution.middleNode(head);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
3.⽤快慢指针判定⼀个linkedlist是否有环。 Be careful about two corner cases: head and tail
链表思想:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/solution/yi-wen-gao-ding-chang-jian-de-lian-biao-wen-ti-h-2/ 图解文字讲解:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/solution/huan-xing-lian-biao-by-leetcode-solution/
JAVA实现
//方法1:hash table
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (head != null) {
if (!seen.add(head)) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}
//方法2:快慢指针
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}
//方法2改进版:快慢指针初试设定也可以设定成 fast = head, slow = head,先移动再判断就可以了
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
//if(head == null || head.next == null) return false;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow) return true; // 先移动再判断,避免两个都在head还没移动的情况
}
return false; // fast == null || fast.next == null
}
}
4.环路检测 题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-lcci/ 题解数学证明:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-lcci/solution/kuai-man-zhi-zhen-zheng-ming-bi-jiao-yan-jin-by-ch/ 题解:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-lcci/solution/huan-lu-jian-ce-by-leetcode-solution-s2la/
JAVA实现
//我的解法
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
fast = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
5.有序链表中插入节点 Insert a node in a sorted linked list
6.合并两个有序链表 Merge two sorted linkedlist into one long sorted linked list
JAVA实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
//When we want to append new elements to an initially empty linkedList
//we do not have an initial head node. In this case.
//we can new a dummy node to act as a head node
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = dummyNode;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val <= l2.val){
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
//Java三目运算符
//"(a<b)?a:b"是一个"条件表达式",它是这样执行的:如果a<b为真,则表达式取a值,否则取b值.
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
7. 给定一个单链表 L 的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为 N1 → N2 → N3 → N4 → N5 → N6→……→Nn→ null
(convert to) (N1 → Nn) → (N2 → Nn-1) → …
思路: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-list/solution/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-by-34/ 第一步:找中点。可以快慢指针的方法。快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,当快指针走到终点的话,慢指针会刚好到中点。如果节点个数是偶数的话,slow 走到的是左端点,利用这一点,我们可以把奇数和偶数的情况合并,不需要分开考虑。
第二步:链表逆序。有迭代和递归的两种方式,迭代的话主要利用两个指针,依次逆转。
第三步:两个指针分别向后移动就可以。
JAVA实现
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return;
}
//找中点,链表分成两个
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode newHead = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
//第二个链表倒置
newHead = reverseList(newHead);
//链表节点依次连接
while (newHead != null) {
ListNode temp = newHead.next;
newHead.next = head.next;
head.next = newHead;
head = newHead.next;
newHead = temp;
}
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode tail = head;
head = head.next;
tail.next = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode temp = head.next;
head.next = tail;
tail = head;
head = temp;
}
return tail;
}
参考: Java ListNode链表: https://www.cnblogs.com/easyidea/p/13371863.html ArrayList和LinkList区别: https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/news/700913 链表ListNode及其常用方法实现: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41437542/article/details/108768900 Java中的链表及ListNode超详解: https://blog.csdn.net/m0_48256515/article/details/114750607
</font>