Sort Array
Sort Array
排序数组Leetcode官方解答: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-an-array/solution/pai-xu-shu-zu-by-leetcode-solution/
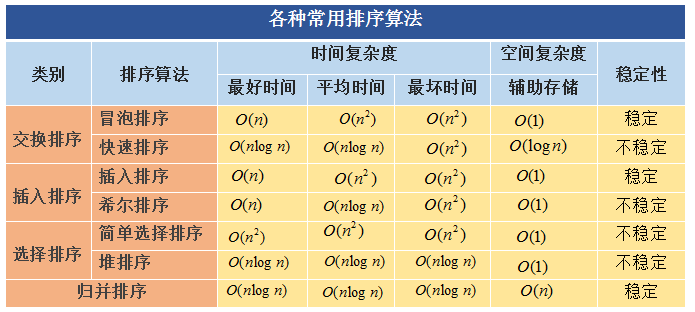
排序算法复习:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-an-array/solution/fu-xi-ji-chu-pai-xu-suan-fa-java-by-liweiwei1419/
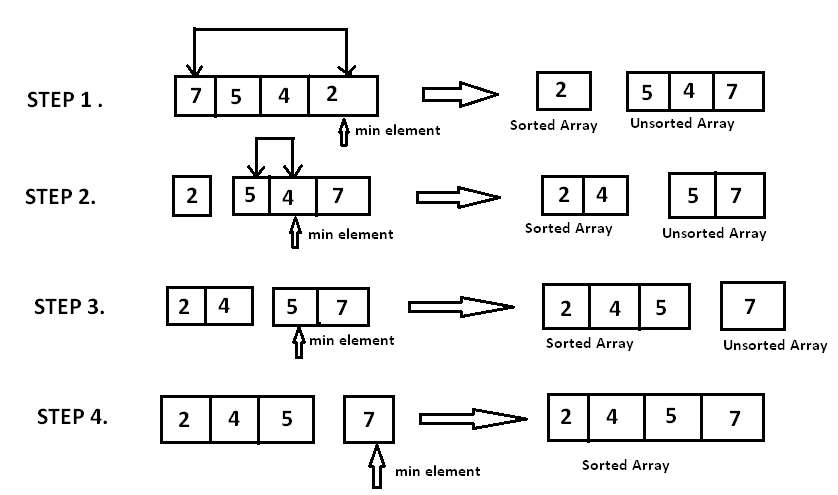
1. Selection Sort
设置一个globalmin,每次找到最小值swap到最前面,用双指针双循环和globalmin解决。
import java.util.Arrays;
//java code for Selection Sort.
class Solution{
public void selectionsort(int[] nums){
int globalmin;
int i, j;
int temp;
for(i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++){
globalmin = i;
for(j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++){
if(nums[j] < nums[globalmin]){
globalmin = j;
}
}
temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[globalmin];
nums[globalmin] = temp;
}
}
}
public class SelectionSort{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] array = {3,5,1,6,2,8,-8,-3,0};
Solution ss = new Solution();
ss.selectionsort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
Time Complexity: O(n^2)
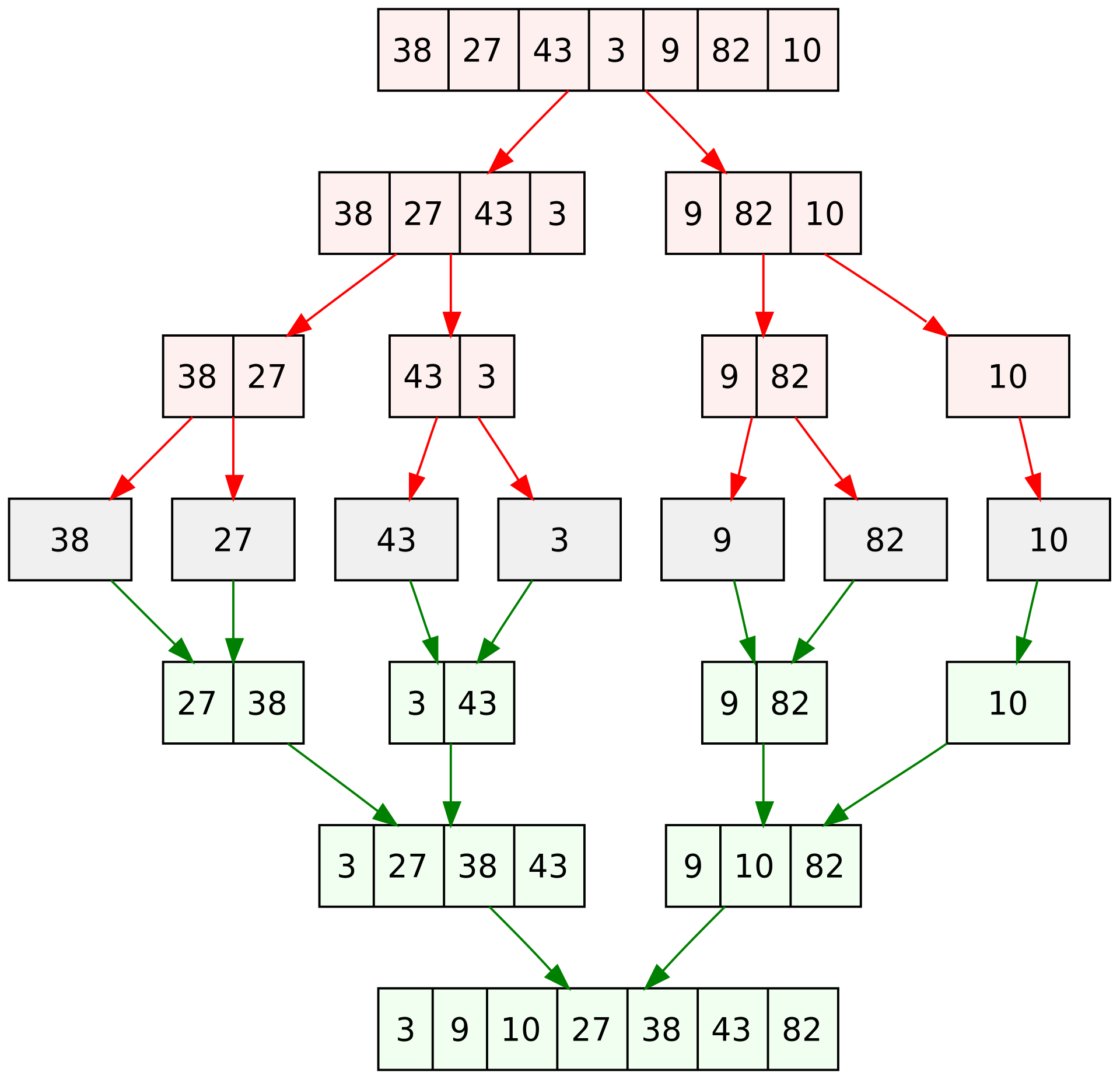
2. Merge Sort
不停二分到最小再整合排序。
import java.util.Arrays;
//java code for Merge Sort.
//Method 1
class Solution{
public void mergesort(int[] nums, int l, int r){
if(l == r){
return;
}
else{
int mid = l + (r - l)/2;
mergesort(nums, l, mid);
mergesort(nums, mid + 1, r);
merge(nums, l, mid, r);
}
}
public void merge(int[] nums, int left, int mid, int right){
int[] temp = new int[right - left + 1];
int i = left;
int j = mid + 1;
int k = 0;
//把较小的数先移到新数组中
while(i <= mid && j <= right){
if(nums[i] < nums[j]){
temp[k++] = nums[i++];
} else {
temp[k++] = nums[j++];
}
}
//把左边剩余的数移入数组
while(i <= mid){
temp[k++] = nums[i++];
}
//把右边剩余的数移入数组
while(j <= right){
temp[k++] = nums[j++];
}
//把新数组中的数覆盖nums数组
for(int m = 0; m < temp.length; m++){
nums[m + left] = temp[m];
}
}
}
public class MergeSort{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] array = {2,4,6,3,8,9,1,5,7};
Solution ms = new Solution();
ms.mergesort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
//java code for Merge Sort.
//Method 2
public void mergeSort (int[] list, int lowIndex, int highIndex) {
if (lowIndex == highIndex)//Recursion base case
return;
else {
int midIndex = (lowIndex + highIndex) / 2;
mergeSort(list, lowIndex, midIndex);
mergeSort(list, midIndex + 1, highIndex);
merge(list, lowIndex, midIndex, highIndex);
}
}
public void merge(int[] list, int lowIndex, int midIndex, int highIndex) {
//新建一个数组用来存储二分后左边数组,+2是为了防止溢出,让最后一个数永远有可比的数
//正常全部存储的长度应该为[midIndex - lowIndex + 1],增加一位存入数组能存入的最大值
//确保其大于或等于数组中的数
int[] L = new int[midIndex - lowIndex + 2];
for (int i = lowIndex; i <= midIndex; i++) {
L[i - lowIndex] = list[i];
}
L[midIndex - lowIndex + 1] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//新建一个数组用来存储二分后右边数组
int[] R = new int[highIndex - midIndex + 1];
for (int i = midIndex + 1; i <= highIndex; i++) {
R[i - midIndex - 1] = list[i];
}
R[highIndex - midIndex] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int i = 0, j = 0;
//将左右数组进行排序后存回原数组相应位置
for (int k = lowIndex; k <= highIndex; k++) {
if (L[i] <= R[j]) {
list[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else {
list[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
}
}
Time complexity = O(nlogn)
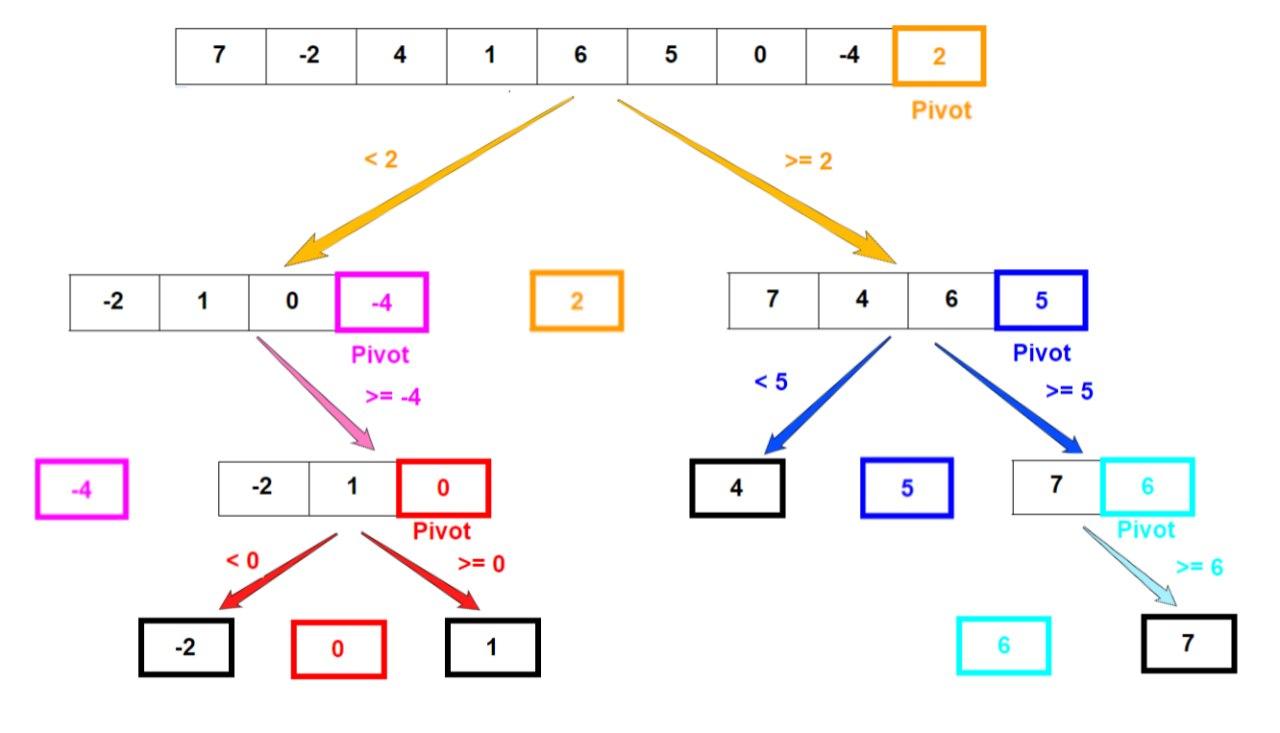
3. Quick Sort
两个挡板 i, j ,三个区域 a, b, c 的思想:
a. [0, i): i 的左侧 (不包括i) 全部为比pivot小的数
b. [i, j): i 和 j 之间为未知探索区域
c. (j, n-1]: j 的右侧 (不包含j) 全部为比pivot大或等于的数字
#一般取array最右的数开始进行快排
//方法一:
class Solution{
//交换array中两个数字的位置
public void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
//将pivot移到它在数组中应该在的位置
//使其左边都是比它小的数,其右边都是比它大的数
//最后返回排好序的pivot的位置
private int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high){
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++){
if(arr[j] < pivot){
i++;
swap(arr, i, j);
}
}
swap(arr, i + 1, high);
return (i + 1);
}
//根据返回的之前的pivot的位置,将数组二分,并继续进行二分直至不可分
public void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high){
if(low < high){
int pi = partition (arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
//打印数组的function
public void printArray(int[] arr)
{
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//主函数,Driver Code
public class QuickSort{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {7,1,2,8,3,5,4,6,9};
int n = arr.length;
Solution qs = new Solution();
qs.quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
qs.printArray(arr);
}
}
//结果:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
//方法二:
class Solution {
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
return Arrays.copyOf(arr, k);
}
private void quickSort(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
// 子数组长度为 1 时终止递归
if (l >= r) return;
// 哨兵划分操作(以 arr[l] 作为基准数)
int i = l, j = r;
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && arr[j] >= arr[l]) j--;
while (i < j && arr[i] <= arr[l]) i++;
swap(arr, i, j);
}
swap(arr, i, l);
// 递归左(右)子数组执行哨兵划分
quickSort(arr, l, i - 1);
quickSort(arr, i + 1, r);
}
private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class QuickSort {
public void quickSort(int[] A) {
quickSort(A, 0, A.length-1);
}
private void quickSort(int[] A, int low, int high) {
if (low < high+1) {
int p = partition(A, low, high);
quickSort(A, low, p-1);
quickSort(A, p+1, high);
}
}
private void swap(int[] A, int index1, int index2) {
int temp = A[index1];
A[index1] = A[index2];
A[index2] = temp;
}
// returns random pivot index between low and high inclusive.
private int getPivot(int low, int high) {
Random rand = new Random();
return rand.nextInt((high - low) + 1) + low;
}
// moves all n < pivot to left of pivot and all n > pivot
// to right of pivot, then returns pivot index.
private int partition(int[] A, int low, int high) {
swap(A, low, getPivot(low, high));
int border = low + 1;
for (int i = border; i <= high; i++) {
if (A[i] < A[low]) {
swap(A, i, border++);
}
}
swap(A, low, border-1);
return border-1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
QuickSort qs = new QuickSort();
int[] A = {9, 0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 9, 1, 0, 9};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(A));
qs.quickSort(A);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(A));
}
}
Time complexity = O(nlogn)